Graphs in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
A graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes (also called vertices) and edges that connect pairs of nodes. Graphs are used to model relationships between objects in a wide range of problems, from social networks to road maps and network routing.
Key Terminology
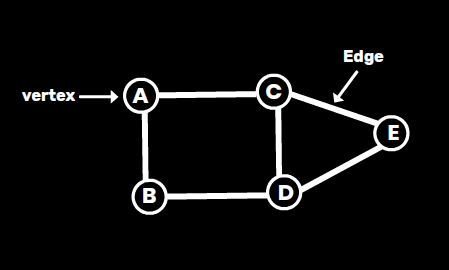
- Vertex (Node): Represents an entity in the graph.
- Edge: Represents a connection or relationship between two vertices.
- Adjacency: Two vertices are adjacent if they are connected by an edge.
- Degree of a Vertex:
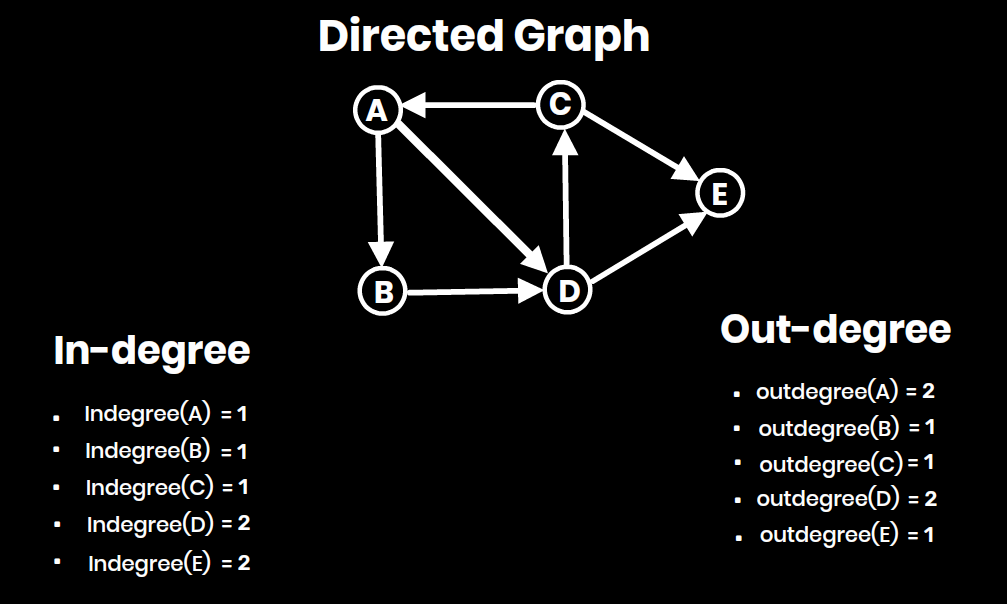
- In-degree: Number of incoming edges to a particular vertex (for directed graphs).
- Out-degree: Number of outgoing edges from a particular vertex (for directed graphs).
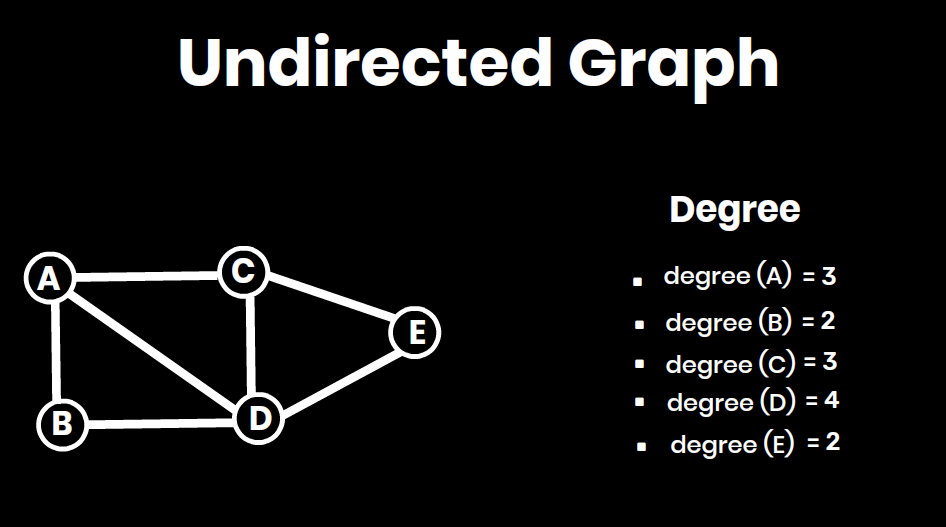
- Degree: Total number of edges connected to the vertex (for undirected graphs).
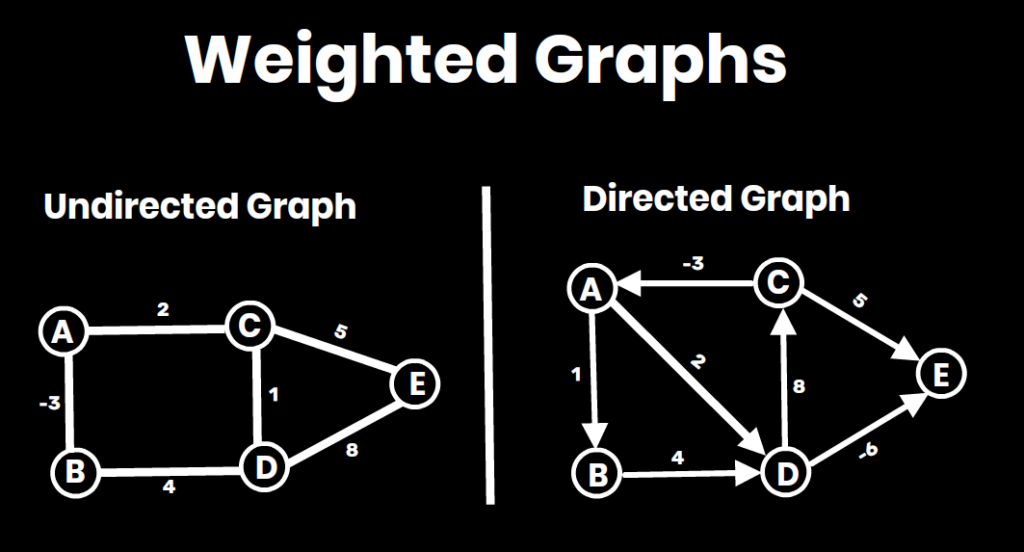
5. Weight: A value (cost, distance, etc.) associated with an edge in a weighted graph. A weighted graph can be either directed or undirected, and the weights of the edges can be either positive or negative.