Common Graph Algorithms
- Shortest Path Algorithms:
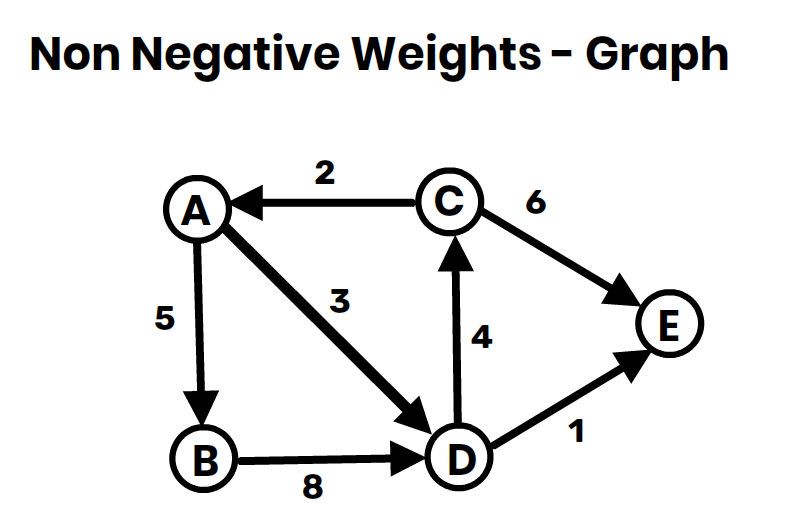
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm: For graphs with non-negative weights.
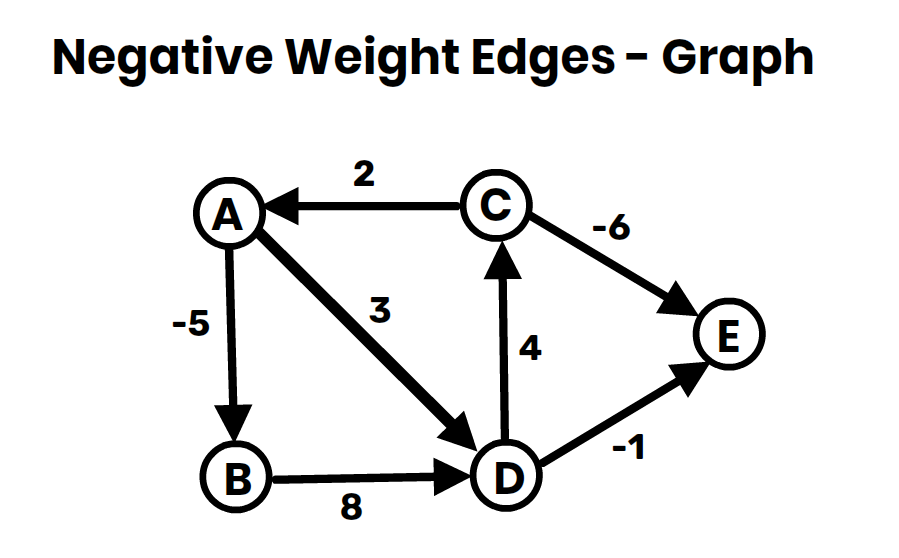
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm: Handles negative weight edges.
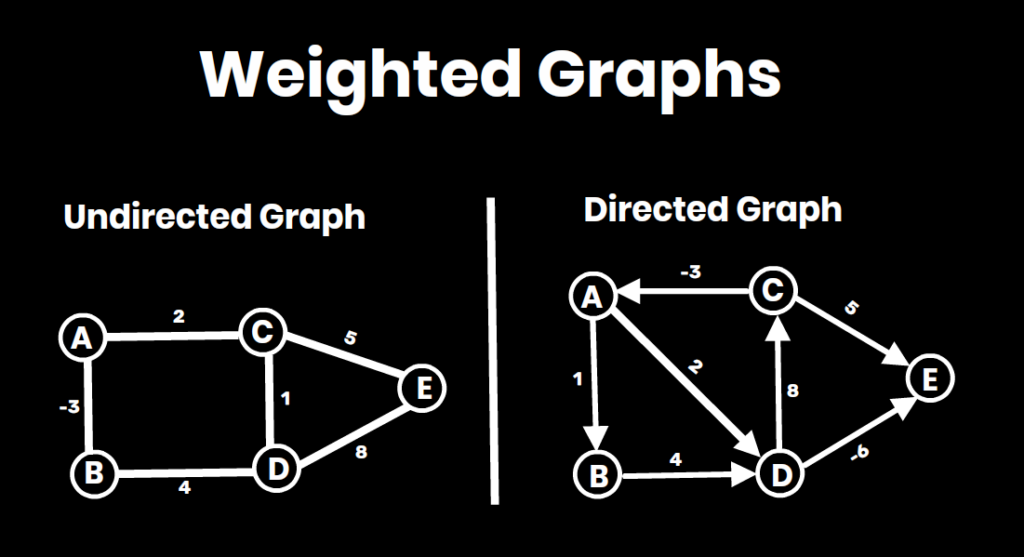
- Floyd-Warshall Algorithm: For all-pairs shortest paths (means to calculate the shortest paths between every pair of vertices in a weighted graph).
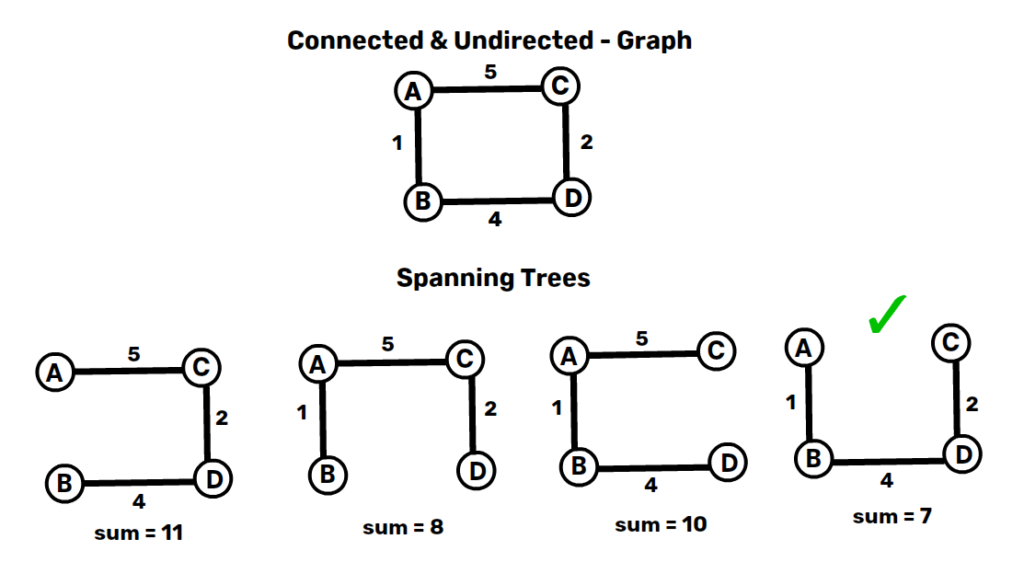
2. Minimum Spanning Tree (MST):
- Kruskal’s Algorithm: Greedy algorithm for MST.
- Prim’s Algorithm: Another greedy algorithm for MST.
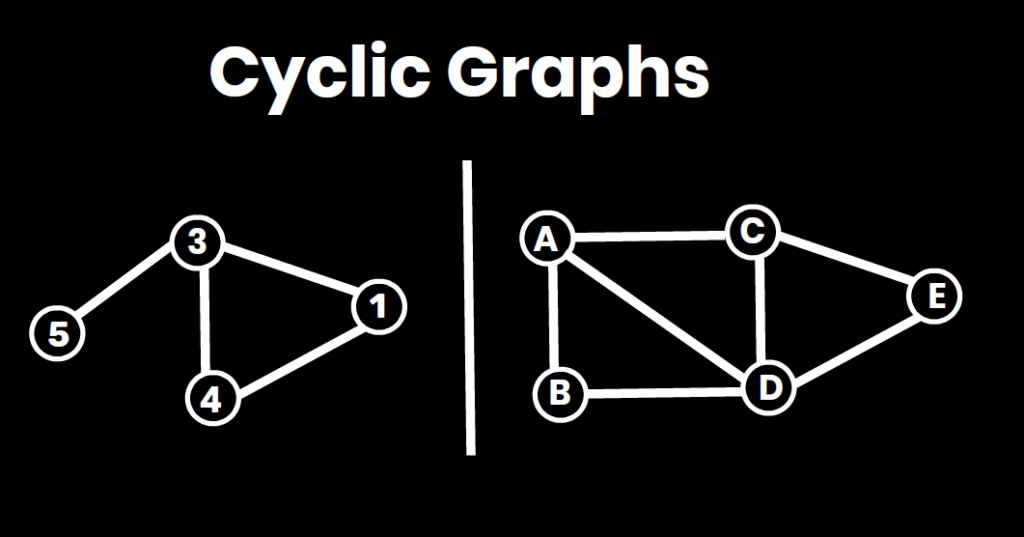
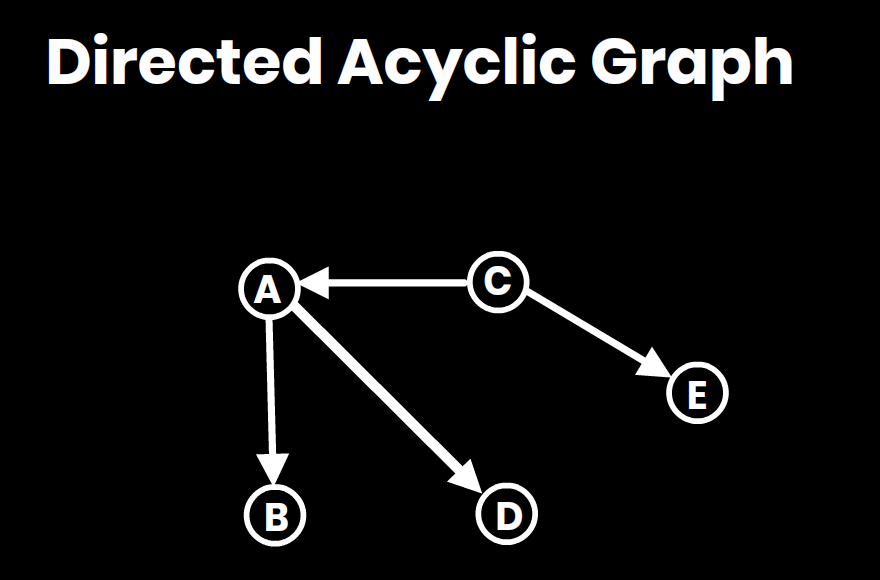
3. Cycle Detection:
- Detects if a graph contains cycles (used in detecting deadlocks, checking DAGs, etc.).
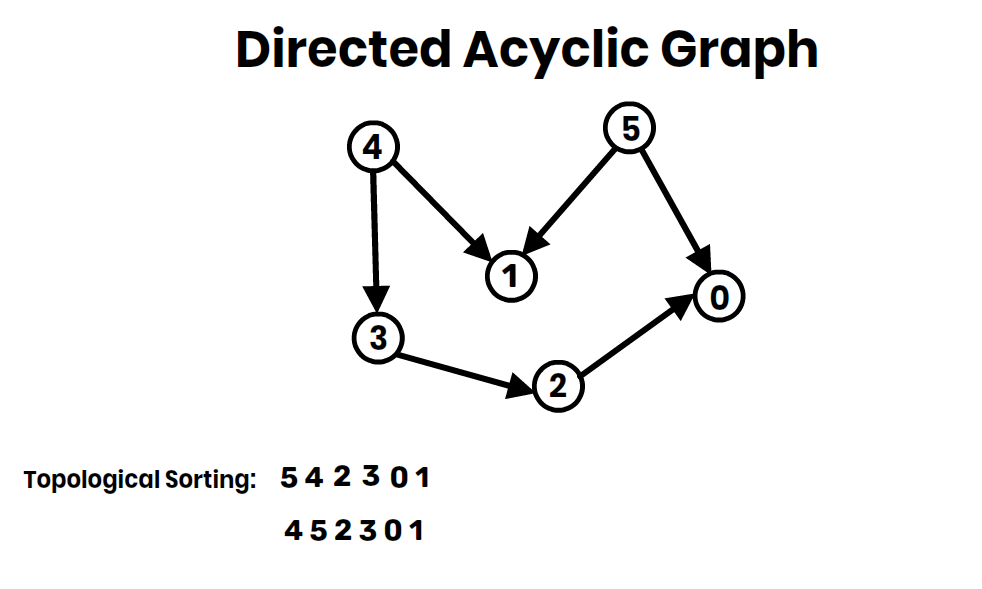
4. Topological Sorting:
- Linear ordering of vertices in a DAG (The first vertex in a topological sort is always a vertex with an in-degree of 0, meaning it has no incoming edges).
5. Connected Components:
- Identifies distinct subgraphs in an undirected graph.
- Subgraph:
- A subgraph is a part of the original graph that consists of a subset of vertices and the edges connecting them.
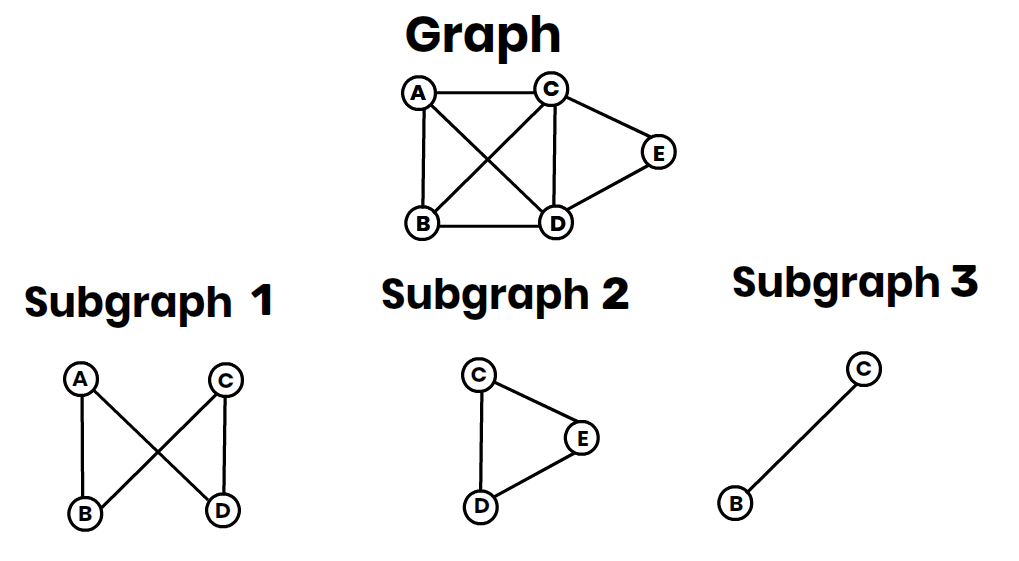
- Distinct Subgraphs:
- Two subgraphs are said to be distinct if there are no edges connecting any vertex in one subgraph to any vertex in the other subgraph.
